The semiconductor industry has played a key role in the modern economy, not merely as a technical field but also as a critical pillar of global technological development. This industry supplies essential components for electronic devices, from mobile phones and computers to cars and smart home appliances. These components are not just tiny parts of a device; they are the key factors determining the performance, connectivity, and features of the product.
Overview of the Semiconductor Industry
General Concept
Semiconductor technology forms the foundation for the development of many advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. These technologies require rapid and efficient information processing, which can only be achieved through advanced semiconductor components. Semiconductors, essentially, are materials that can conduct electricity partially, allowing for flexible control of current and signals. This capability not only enables the creation of complex integrated circuits but also opens doors to developing high-tech products and applications.
The growth of the semiconductor industry also reflects continuous progress in material science. Researchers and engineers are working to enhance the performance of semiconductor materials, from traditional silicon to new materials like graphene and other semiconductor compounds. These advancements not only help reduce the size of components but also improve durability and energy efficiency, contributing to the development of modern electronic devices used daily.
From basic electronic devices to complex technologies, the semiconductor industry has truly shaped the overall picture of modern life. These products not only meet personal needs but also drive economic and social development, creating millions of jobs and contributing to the sustainable growth of the global economy.
Semiconductor Supply Chain
The semiconductor industry comprises several stages, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the quality and performance of the final products.
Stage 1: Design
At this stage, engineers and designers use specialized software to develop integrated circuits based on specific product requirements. Beyond merely creating circuit diagrams, the design phase includes simulation and testing processes to ensure the design will function effectively in real-world conditions.
Integrated circuit design—a crucial part of the production process—involves creating integrated circuits on a semiconductor chip. This process accounts for approximately 50-60% of the value of a finished chip. During this stage, engineers systematically select electronic components and connect them to perform essential functions determined by the specific needs of the product.
Circuits are designed with a priority on using the minimum number of components to reduce costs while ensuring minimal size and high reliability. These designs must also remain stable under various environmental conditions. FPT Semiconductor plays an important role in the chip supply chain, handling the initial stage by creating the design, considered the “soul” of the chip, embodying the intelligence and hard work of the engineering team.
Stage 2: Fabrication
After completing the design phase, the product moves to the fabrication stage. Here, semiconductor materials are processed and fabricated into specific electronic components. This process typically involves multiple complex steps, such as cleaning, etching, and thin-film coating, requiring advanced technology and equipment. The fabrication stage is one of the most expensive stages in the production chain and demands absolute precision.
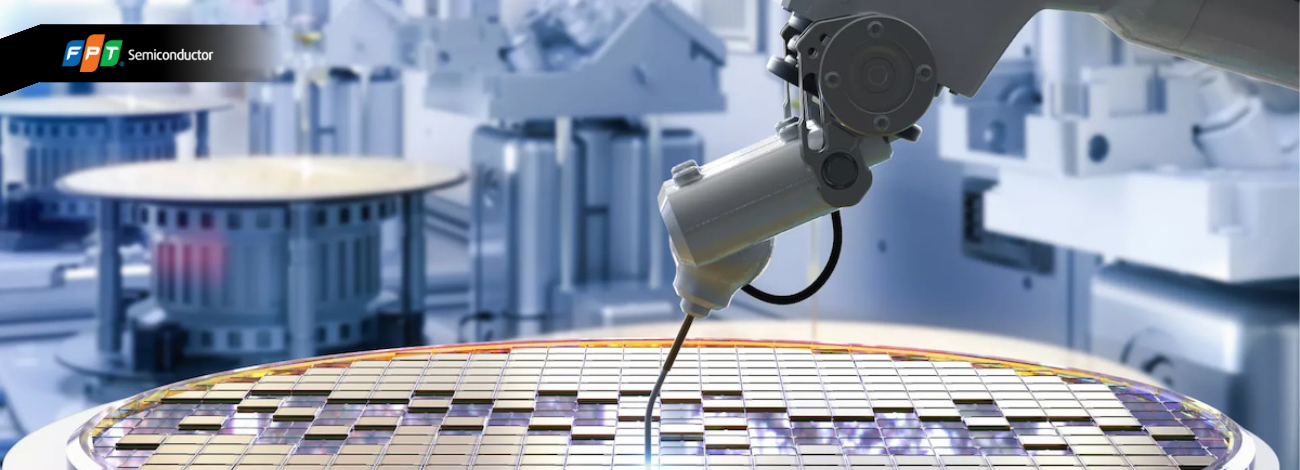
Chip fabrication is a chip design into a physical chip that can be seen and held. A crucial element in this stage is fabricating the wafer (or semiconductor silicon wafer), which serves as the “container” to etch the chip design. The fabrication process includes the following steps:
- Wafer preparation
- Wafer surface treatment
- Oxidation
- Diffusion
- Photolithography
- Ion implantation
- Etching
- Wafer cleaning
- Parameter testing
- Wire bonding
- Chip bonding onto the substrate
Each step ensures that the produced electronic components meet the highest quality standards.
Stage 3: Packaging
The packaging stage follows fabrication, where semiconductor components are protected and prepared for delivery to end-users and other manufacturers. Packaging is not merely wrapping up the product; it is a complex technical process to ensure components can operate stably and durably throughout their use. Modern packaging technology also enhances heat dissipation, saves space, and improves the overall performance of electronic devices.
During packaging, the chips fabricated in the previous stage are layered and assembled into packages that can be mounted on circuit boards. Once completed, these packages undergo surveys and evaluations under various electrical and thermal conditions to ensure quality before being integrated into the final product.
Stage 4: Integration & Consumption
In this stage, semiconductor components are assembled into final electronic devices, such as phones, computers, and various other products. This process requires smooth coordination between manufacturers and suppliers to ensure the best quality products reach consumers. Furthermore, consumers play a vital role in driving the semiconductor industry through the increasing demand for electronic devices.
During the integration and consumption stage, after packaging is completed, electronic device manufacturers integrate the chips into electronic circuits, thus creating the final product for consumers. These products are then distributed to companies, retailers, and consumers worldwide, serving various purposes and completing the cycle in the chip supply chain.
Global and Vietnamese Semiconductor Market Overview
Market Context
The transformation of the semiconductor market affects not only chip manufacturers but also various sectors such as automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. In this context, Vietnam is also striving to establish its position in the global semiconductor supply chain. Analyzing the worldwide and Vietnamese semiconductor market context helps us better understand the trends, opportunities, and challenges in this industry.
Global Market
The global semiconductor industry is experiencing rapid growth, with increasing applications of semiconductor technology in various fields. According to market reports, global semiconductor revenues are expected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in the coming years, with an impressive Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). This growth is mainly driven by the rising demand for chips for smart devices, mobile phones, computers, and IoT applications.
One of the key drivers of the semiconductor market’s growth is the explosion of 5G technology. This technology improves data transmission speeds and opens opportunities for new applications, from autonomous vehicles to smart city systems. Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an indispensable part of chip design and manufacturing, requiring semiconductor components that consume low power but still deliver high performance.

The semiconductor market is also witnessing a shift in production from traditional regions to new locations. Countries like Taiwan, South Korea, and China play pivotal roles. These companies are seeking investment opportunities in places with lower labor costs and more favorable investment environments, creating a new competitive landscape in the global semiconductor industry.
Vietnamese Market
In Vietnam, the semiconductor industry is in a robust growth phase with notable opportunities. The Vietnamese government has implemented policies to promote foreign investment in high-tech industries, including the manufacturing and production of semiconductor components. Thanks to a young workforce, competitive labor costs, and an increasingly favorable investment environment, Vietnam is attracting the attention of many foreign investors.
Currently, Vietnam hosts several major companies in semiconductor manufacturing, contributing to the global supply chain. However, the Vietnamese semiconductor sector also faces significant challenges, such as a shortage of highly skilled professionals in information technology and semiconductor engineering. Developing quality training programs and attracting talent are essential to enhancing competitive capabilities.
Additionally, Vietnam needs to invest more heavily in research and development (R&D) to create new products and technologies that meet the growing international market demand. Collaborations with universities, research institutes, and large technology companies will help Vietnam improve innovation in the semiconductor sector.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Modern Production Processes
The semiconductor industry is witnessing strong development of advanced manufacturing technologies, notably Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, and 3D Integrated Circuit (IC) technologies.
EUV technology is a breakthrough in chip manufacturing, enabling the creation of integrated circuits with higher precision. By using ultraviolet light with shorter wavelengths than previous technologies, EUV reduces the size of components on a chip, thus enhancing performance and reducing energy consumption. This technology allows manufacturers to produce smaller yet more powerful chips, catering to the increasing market demands.
3D IC is another emerging technology that allows chips to be assembled vertically instead of horizontally, saving space and improving data transmission speeds between chips. 3D IC technology enhances design flexibility and enables the integration of multiple functions into a single chip, optimizing overall electronic system performance.
New technologies like EUV and 3D IC positively impact performance and production costs in the semiconductor industry. First, EUV technology helps reduce component sizes, allowing for higher integration density without compromising performance. This means new chips can perform more functions within the same space, thus improving the overall performance of devices.
Moreover, reducing the size of components also means lower energy consumption, which is crucial as the demand for energy-efficient devices grows. This not only improves performance but also reduces operational costs for consumers.
Regarding 3D IC technology, integrating multiple functions into a single chip reduces the number of required components, thus lowering production costs. Additionally, vertical chip assembly optimizes space and enhances heat dissipation, increasing product reliability and lifespan.
Trends and Challenges in the Semiconductor Industry
Development Trends
The semiconductor industry is currently experiencing prominent development trends that play a key role in shaping the future of technology. Two of the most significant trends in recent times are the boom in artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
AI has become a crucial element in chip design and applications.
The rising demand for AI applications—from image recognition and natural language processing to process automation—requires chips to process data quickly and efficiently. To meet this demand, many chip manufacturers are investing in developing AI-specific integrated circuits optimized for complex machine learning tasks, enhancing processing speed and overall system performance.
Furthermore, IoT is driving the demand for smart connected devices. As the number of sensors, cameras, and smart household devices increases, the need for compact, energy-efficient chips capable of processing information is rising. Modern semiconductor technology meets these demands, enabling IoT devices to operate efficiently in various environments, from smart homes to smart city systems. IoT’s growth creates significant opportunities for chip manufacturers and spurs innovation in product design.
Another notable trend is the automation and robotics in chip manufacturing. Production processes are becoming increasingly automated, enhancing efficiency and minimizing errors. The application of AI in manufacturing also optimizes processes, from chip design to production and testing, contributing to improved product quality and shorter time-to-market.
Global Challenges
While the semiconductor industry is competing with many opportunities, it also faces significant challenges. One of the most severe challenges today is the chip shortage, a pressing issue in recent years, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic disrupted global supply chains and increased demand for electronic devices, leading to a worldwide chip shortage. Manufacturers are struggling to meet market demand, leading to production delays and increased costs for consumers.

Global competition is also a major challenge for the semiconductor industry. With rising investments from countries like China, South Korea, and Taiwan, competitive pressure is intensifying. Companies in these regions continuously innovate and enhance manufacturing technologies, while government protectionist policies and support are driving rapid development in their semiconductor industries. It forces companies in other regions, such as North America and Europe, to enhance their competitiveness through innovation and process optimization.
Additionally, technological and research barriers pose significant challenges. The semiconductor industry requires substantial investments in R&D to keep up with new technologies. A shortage of specialized human resources can hinder the industry’s growth, especially as technology becomes increasingly complex.
Conclusion
In the rapidly changing market context, the semiconductor industry must proactively adapt to development trends while overcoming global challenges. The industry’s progress affects not only itself but also many other sectors of the economy, from manufacturing to consumer goods and services.
This continuous development and innovation reflect technological advancements and the increasing market demand. These advancements create not only new products but also numerous opportunities and challenges for businesses in the future.
To update the latest information, do not forget to follow news about the semiconductor industry right at FPT Semiconductor!
————————————————————————
Contact For Us:
FPT Semiconductor – Chip make in Vietnam made by FPT
Email: [email protected]
Linkedln: https://www.linkedin.com/company/fpt-semiconductor/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/FPT.Semiconductor
Address: FPT Tower, No. 10 Pham Van Bach Street, Dich Vong Ward, Cau Giay District, Hanoi
#SemiconductorFuture #FPTSemiconductor